Ever heard of burgernomics? It is a compilation of the price of Big Macs in all countries around the world (except India), first published not-so-seriously by The Economist in 1986. It is intended to show the purchasing power of the average person in each of these countries using the purchasing power parity 1 (PPP) theory. Why the Big Mac? Because it is perceived to be a standardized food product through out the world in terms of quality and taste, hence the price of the Big Mac tells a lot about its unit cost and the ability of each average person is willing to pay for it in any given country (except India- there are no Big Macs in India, only Maharaja Macs because cows are sacred there; chicken and lamb is used as beef substitute). The Economist magazine also produces other indexes such as Starbucks's Tall Latte index, and the Coke index.
Left: The Chicken Maharaja Mac
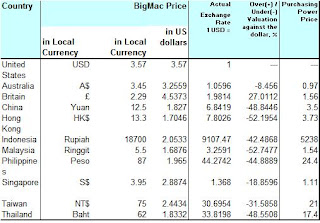
The left shows the Big Mac Index of a few of my favorite countries. Let's take a look at Malaysia and USA; what this index tells us about the Ringgit.
Formula for the Big Mac Index
= (PPP- forex rate)/forex rate
=[(5.5/3.57)-3.2591]/3.2591
=-52.75%
Above: The Big Mac Index of a few countries
The negative 52.75% tells us that the Ringgit for a Big Mac is 52.75% undervalued compared to the USD.
Of course there are critisms against the Big Mac Index:
- the Big Mac is expensive in countries other than the USA and this may not give a true indication of the PPP ie it is not a mainstream cheap meal in India as compared to USA.
- different levels of competition in different countries, different tax structure and culture acceptance will affect the pricing of the Big Mac.
Despite the criticisms, the Big Mac Index still tells us a lot of a particular economic conditions!
1 Purchasing Power Parity- created by Gustav Cassel 1920. A product assuming that it is available throughout the world should only have one price. But because of the imperfect world, different economic conditions in each country influence each of their foreign exchange rate resulting in that particular product being priced differently. The PPP compares the price of the same basket of goods in different countries. The argument is that the price for the same basket of goods should be the same in any given country but otherwise priced, because of the differences in inflation and cost of living in the different countries. The full 2008 Big Mac Index is as below:


No comments:
Post a Comment